1. MaterialLibraryModel
A MaterialLibraryModel is a database containing a list of MaterialModel.
| Name | Return | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GetMaterialByDescription() | MaterialModel | Access to a materialModel by its description (param1) |
| MaterialDescriptionExists() | bool | Return True if a material exists with this description (param1) |
| SetRefTemperature() | - | Set the reference temperature (param1) for all materials [°C in metric units] |
| SetThermalExpansionOption() | - | Set the thermal expansion option (param1) for all materials (0, 1 or 2 by default) - see below |
| AddMaterial() | MaterialModel | Add an empty materialModel to the library (without description) |
| DeleteMaterial() | - | Delete the materialModel (param1) from the library |
| Save() | - | Save the library |
ThermalExpansionOption values :
- 0 : Linear thermal expansion (LTE)
- 1 : Mean coefficient calculated by linear interpolation of LTE values
- 2 : Mean coefficient calculated by linear interpolation of submitted values of α
1.1 MaterialModel
A MaterialModel represents the definition of a material.
| Name | Return | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Description | The description of the material | |
| MaterialType | The type of material | |
| MaxTemperature | Temperature max [°C in metric units] | |
| RO | Density [kg/m³ in metric units] | |
| SG | Poisson’s ratio | |
| Properties | List of MaterialProperties | |
| Properties.Count | int | Number of MaterialProperties |
| Properties.[i] | MaterialProperties | ith MaterialProperties |
| AddProperties() | MaterialProperties | Add a new line of properties for a temperature |
| Deleteproperties() | - | Delete a MaterialProperties (param1) |
1.2 MaterialType
To access the MaterialType property of a MaterialModel, you need to import the object from Cwantic.MetaPiping.Core :
# Python script
from Cwantic.MetaPiping.Core import MaterialType
| Values : |
|---|
| MaterialType.CarbonSteel |
| MaterialType.LowAlloySteel |
| MaterialType.MartensiticSteel |
| MaterialType.AusteniticSteel |
| MaterialType.NickelChromeSteel |
| MaterialType.NickelCopperSteel |
| MaterialType.Other |
| MaterialType.Composite |
| MaterialType.HDPE |
Example :
# Python script
from Cwantic.MetaPiping.Core import MaterialType
...
if mat.MaterialType == MaterialType.CarbonSteel:
...
1.3 MaterialProperties
| Property | Description | Unit Metric | Unit USA |
|---|---|---|---|
| TE | Temperature | °C | °F |
| EH | Modulus of Elasticity | kN/mm² | 10^6.psi |
| EX | Thermal Expansion | 10^-6.mm/mm/°C | 10^-6.in/in/°F |
| SH | Non-Class 1 Allowable Stress | N/mm² | ksi |
| SY | Yield Stress | N/mm² | ksi |
| SU | Ultimate Tensile Stress | N/mm² | ksi |
| SM | Class 1 Allowable Stress | N/mm² | ksi |
| CR | Creep | N/mm² | ksi |
| GH | Shear Modulus | kN/mm² | 10^6.psi |
| CO | Class 1 Thermal Conductivity | kJ/hr/m/°C | btu/hr/ft/°F |
| DI | Class 1 Thermal Diffusivity | mm²/s | ft²/hr |
1.4 Example 1
User wants to get the first temperature of a specific MaterialModel (Inputs[1]) from a specific library (Inputs[0]). Result as a text in Outputs[0].
# Python script
libname = study.Inputs[0]
matname = study.Inputs[1]
lib = study.getMaterialLibraryModel(libname)
if lib != None:
mat = lib.GetMaterialByDescription(matname)
if mat != None:
study.Outputs[0] = str(mat.Properties[0].TE)
else:
study.Outputs[0] = "Material not found !"
else:
study.Outputs[0] = "Library not found !"
1.5 Example 2
User wants to create a material library with a name (Inputs[1]) and only one material (Inputs[3]) with 2 temperatures. Result as a text in Outputs[0].
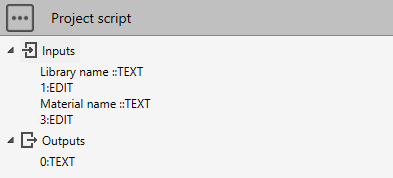
# Create a material library with one material
# © Cwantic
from Cwantic.MetaPiping.Core import MaterialType
libname = study.Inputs[1]
matname = study.Inputs[3]
# Check the input values
if libname != "" and matname != "":
# Check that libname doesn't already exist
lib = study.getMaterialLibraryModel(libname)
if lib == None:
# Create the library with common properties for all materials
lib = study.createMaterialLibraryModel(libname)
lib.SetRefTemperature(20.0)
lib.SetThermalExpansionOption(0)
# Add one material to library
mat = lib.AddMaterial()
mat.Description = matname
mat.MaterialType = MaterialType.AusteniticSteel
mat.MaxTemperature = 500
mat.RO = 7000
mat.SG = 0.3
# Add all properties to material for temp 20
properties = mat.AddProperties()
properties.TE = 20
properties.EH = 200
properties.EX = 0
properties.SY = 215
properties.SH = 153.3
# Add all properties to material for temp 500
properties = mat.AddProperties()
properties.TE = 500
properties.EH = 159.3
properties.EX = 9.25
properties.SY = 109
properties.SH = 72.7
# Save library
lib.Save()
study.Outputs[0] = "OK"
else:
study.Outputs[0] = "Library already exists !"
else:
study.Outputs[0] = "Invalid names !"