Concentric reducer analysis
MetaPiping proposes a detailed analysis of concentric reducer.
After piping analysis, the reducers can be examined.
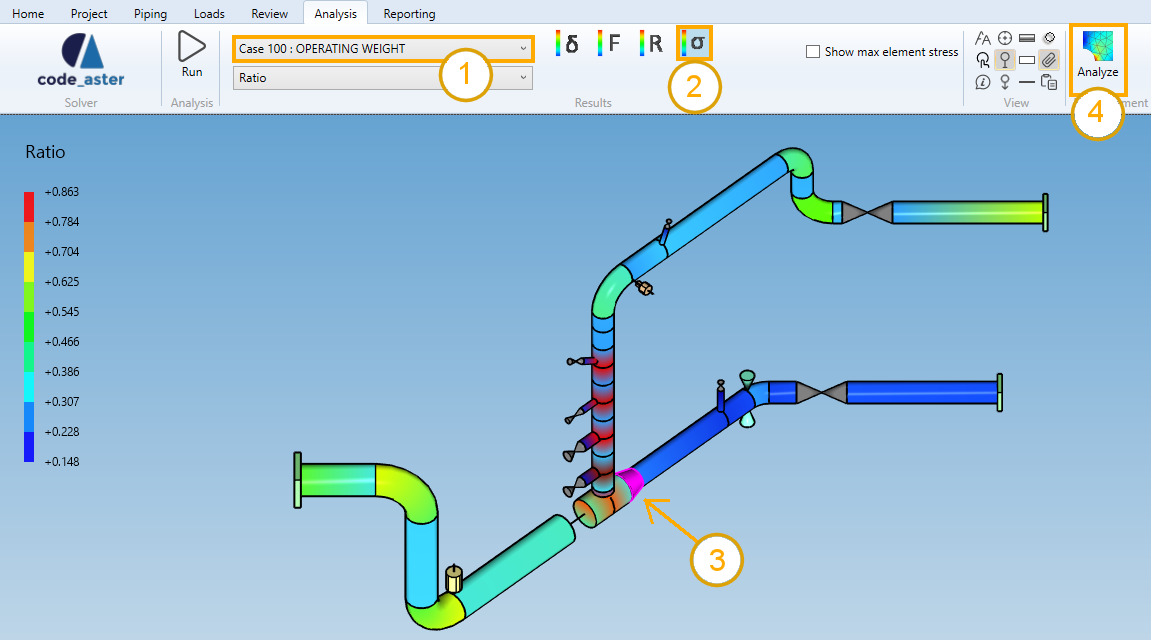
- Select a load case or mode (1).
- Select the stress button (2).
- Select either a reducer in the 3D space or in the results table (3).
- Click on the Analysis button (4).
The selection mode is automatically set to Element when clicking on stress button.
1. Template
Only one template is proposed for the reducer :
- 3D bricks : second order 20-node hexahedrons for curved volumetric element
If other analysis exists for the same Element, the same Load and the same Template, a window will appear.
Example for a pipe analysis (same window for reducers) :
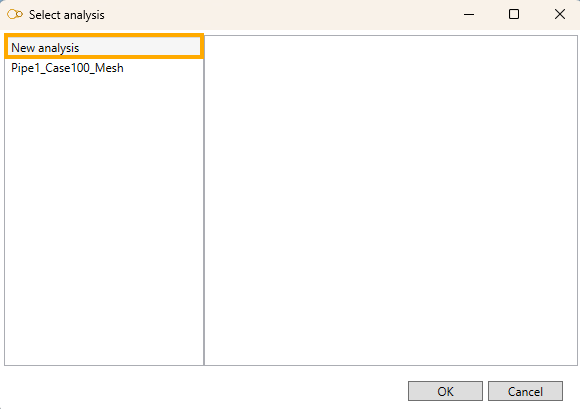
- Select New analysis to start a new analysis from scratch.
- Or select an existing analysis to reopen it :
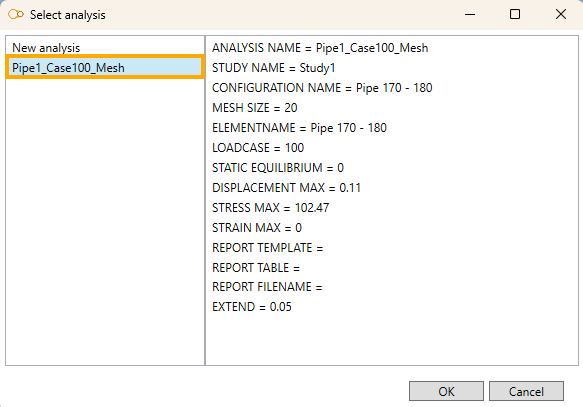
Some properties and results are shown.
Click OK.
2. New analysis
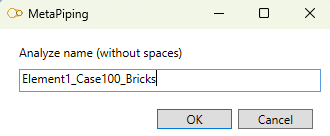
If you choose to create a New analysis, you have to define a name to the analysis (that doesn’t already exist) :
The Finite Element Analysis Window appears (3D brick template).
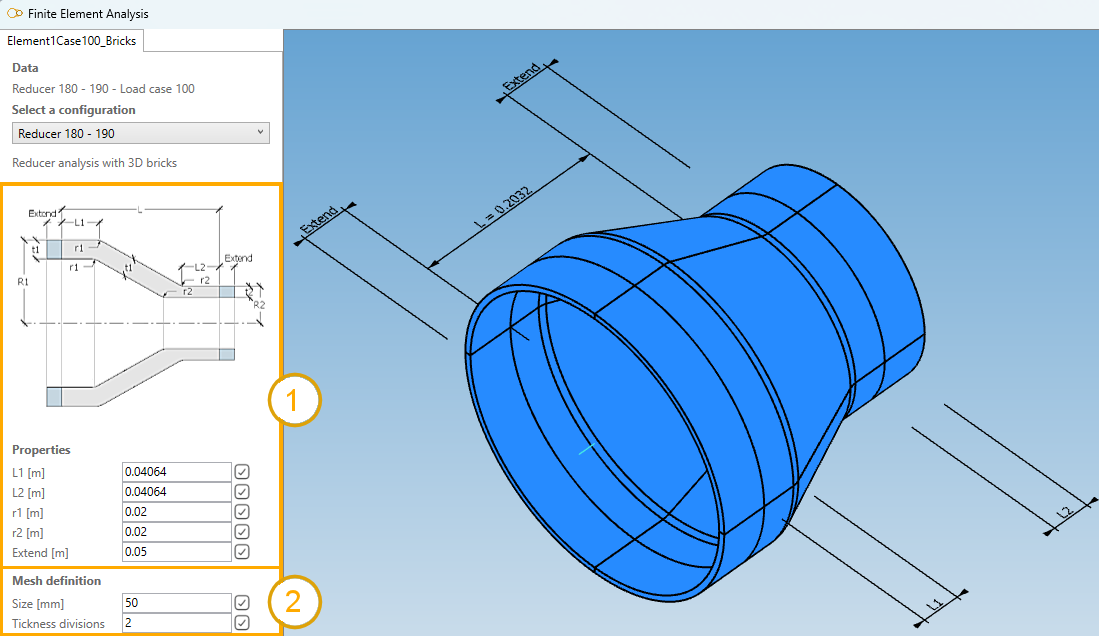
Properties :
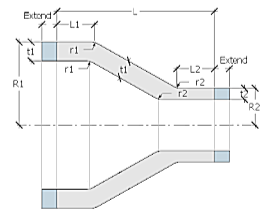
We suppose constant thickness t1 from the larger section.
| Property | Unit Metric | Unit USA | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | m | ft | Horizontal length on the larger diameter |
| L2 | m | ft | Horizontal length on the smaller diameter |
| r1 | m | ft | Transition radius at the larger diameter |
| r2 | m | ft | Transition radius at the smaller diameter |
| Extend | m | ft | Length extension |
Mesh definition :
| Property | Unit Metric | Unit USA | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|
| Size | mm | in | Size of the largest brick side |
| Tickness division | - | - | Number of bricks in the element tickness (min = 1) |
Set these values (1) for example :
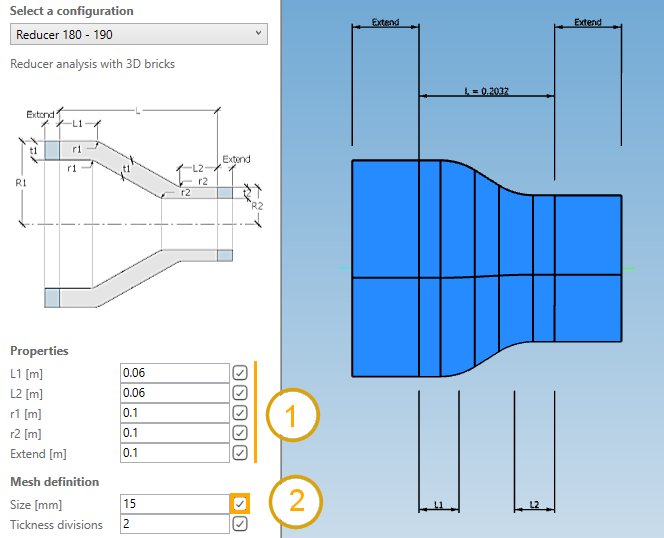
3. Meshing
Choose the mesh size and click on v button (2) :
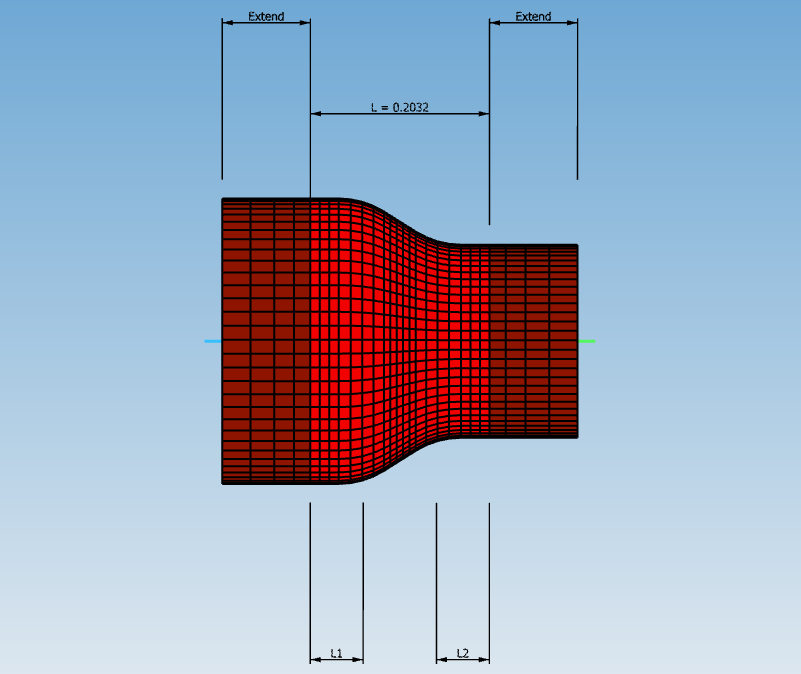
After several seconds, the assembly is totally meshed.
The meshing of the extends follow a geometric progression starting from the extremity of the reducer.
The Code_Aster button is now available for a complete calculation.
4. Finite element analysis
Click on the Code_Aster button to launch a detailed calculation (1):
Colored results appears with a corresponding legend (2) .
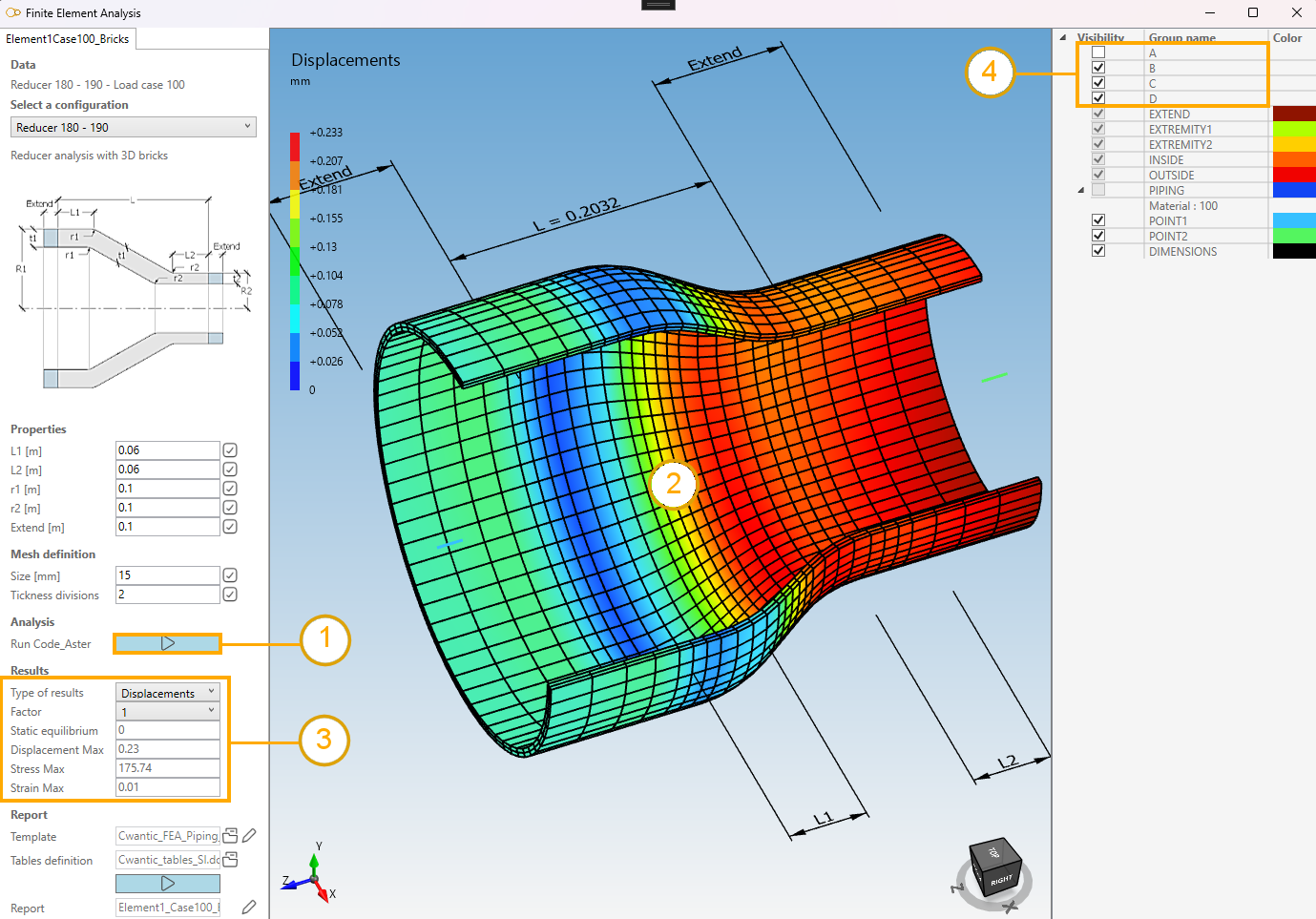
A result panel appears where the type of results can be choose and some informations are shown (3).
Type of results :
| Property | Unit Metric | Unit USA | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|
| Groups | - | - | |
| Displacements | mm | in | Use Factor to amplify the deformation |
| Stresses | N/mm² | ksi | |
| Strains | % | % | |
| Iso-displacements | mm | in | Use Factor to amplify the deformation |
| Iso-stresses | N/mm² | ksi | |
| Iso-Strains | % | % |
The Static equilibrium is also evaluated (value near 0 reaches the perfect equilibrium).
Static Equilibrium refers to the physical state in which a system is at rest and the net force acting
on it is null. It is a state in which all the forces acting on an object are balanced out and the
object is not found to be in motion to the relative plane.
You can select the groups to be shown. Special group A, B, C and D let you hide quarter of the element for a better view (4).
5. Report
A report can be generated based on a template and “tables” file.
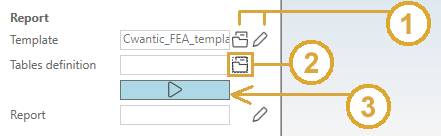
- Select a template (open button) or edit template (pencil button) (1).
- Select a tables file (open button) (2).
- Click on the Report button to generate the report (3).
Use the default template Cwantic_FEA_Piping_template_SI
The template is copy from the settings to the analysis’ directory and can be locally modified before report generation (requires Microsoft Word).
The select document window (example for table) :
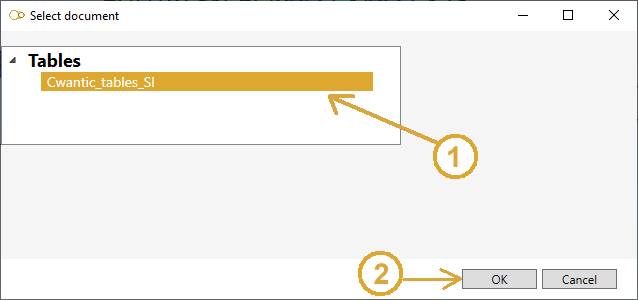
- Select the document (1)
- Click OK (2)
After generation, the report receive the name of the analysis.
You can edit the final report by clicking on the pencil button (requires Microsoft Word) :
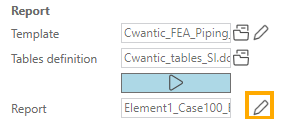
Click here to have more information about the reporting mechanism.
5.1 Keywords
The keyword is useful to make a correspondence between the template and the table document but with specific decorators :
$$keyword$$ for the template
[keyword] for the table
| Keyword | Description | Remark |
|---|---|---|
| STUDY NAME | The name of the current study | No table |
| ANALYSIS NAME | The name of the current analysis | No table |
| PICTURE | Take a picture (§5.2) | No table |
| CONFIG PICTURE | The picture of the current config | No table |
| MESH RESULTS | The list of all mesh results | table [MESH RESULTS] |
| CONFIGURATION NAME | The name of the current configuration | No table |
| ELEMENT PROPERTIES | The element properties | table [ELEMENT PROPERTIES] |
| MESH SIZE | The meshing properties | table [MESH SIZE] |
| ELEMENTNAME | The name of the current element | No table |
| LOADCASE | The current load case | No table |
| STATIC EQUILIBRIUM | The static equilibrium value | No table |
| DISPLACEMENT MAX | The displacement max | No table |
| STRESS MAX | The stress max | No table |
| STRAIN MAX | The strain max | No table |
| FASTENER RATIO MAX | The max ratio on all fasteners | No table |
CONFIG PICTURE for concentric reducer =
5.2 Picture
It is possible to include pictures in the report with use of the keyword PICTURE.
When the software encounters this keyword, it simply makes a screenshot of the 3D engine.
It is possible to change the kind of visualization via a JSON structure just after the keyword separated by a semicolon character :
$$PICTURE;{...}$$
JSON parameters :
| Parameter | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| Groups | An array of visible group name | Empty list = all groups will be visible |
| View | Orientation of the camera | 35 (= FrontFaceTopLeft - see below) |
| ResultType | Result category | 0 (= Group - see below) |
| Factor | Amplification factor of the displacements | 1 |
| Dim | 1 = show dimensions | 1 |
View values :
Front = 0
Right = 1
Rear = 2
Left = 3
Top = 4
Bottom = 5
Isometric = 6
Dimetric = 7
Trimetric = 8
FrontFaceBottom = 9
FrontFaceRight = 10
FrontFaceTop = 11
FrontFaceLeft = 12
RightFaceBottom = 13
RightFaceRight = 14
RightFaceTop = 15
RightFaceLeft = 16
BackFaceBottom = 17
BackFaceRight = 18
BackFaceTop = 19
BackFaceLeft = 20
LeftFaceBottom = 21
LeftFaceRight = 22
LeftFaceTop = 23
LeftFaceLeft = 24
BottomFaceBottom = 25
BottomFaceRight = 26
BottomFaceTop = 27
BottomFaceLeft = 28
TopFaceBottom = 29
TopFaceRight = 30
TopFaceTop = 31
TopFaceLeft = 32
FrontFaceBottomLeft = 33
FrontFaceBottomRight = 34
FrontFaceTopLeft = 35
FrontFaceTopRight = 36
BackFaceBottomLeft = 37
BackFaceBottomRight = 38
BackFaceTopLeft = 39
BackFaceTopRight = 40
Result type values :
Group = 0
Displacement = 1
Stress = 2
Strain = 3
Compression = 4
IsoDisplacement = 5
IsoStress = 6
IsoStrain = 7
IsoCompression = 8
Example for this displacement view :
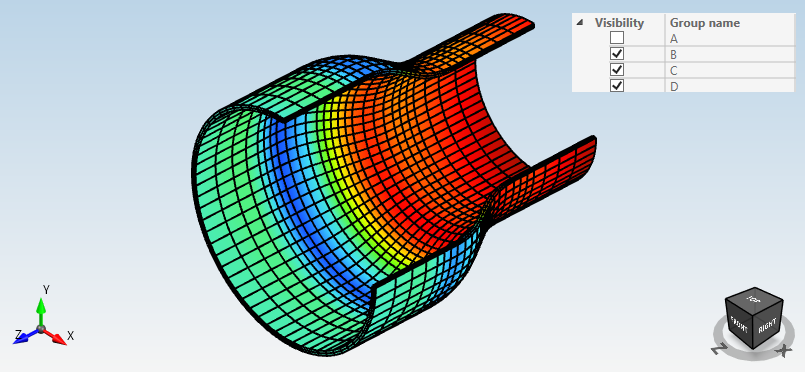
$$PICTURE;{“ResultType”:1,“View”:36,“Dim”:0,“Groups”:[“B”,“C”,“D”]}$$
ResultType = 1 for a “Displacement” view
View = 36 for a FrontFaceTopRight view (Only TOP + FRONT + RIGHT faces of the gray cube are visible)
Dim = 0 will hide the dimensions
Groups = [“B”, “C”, “D”] will show only these groups (and not “A”)
5.3 Word result
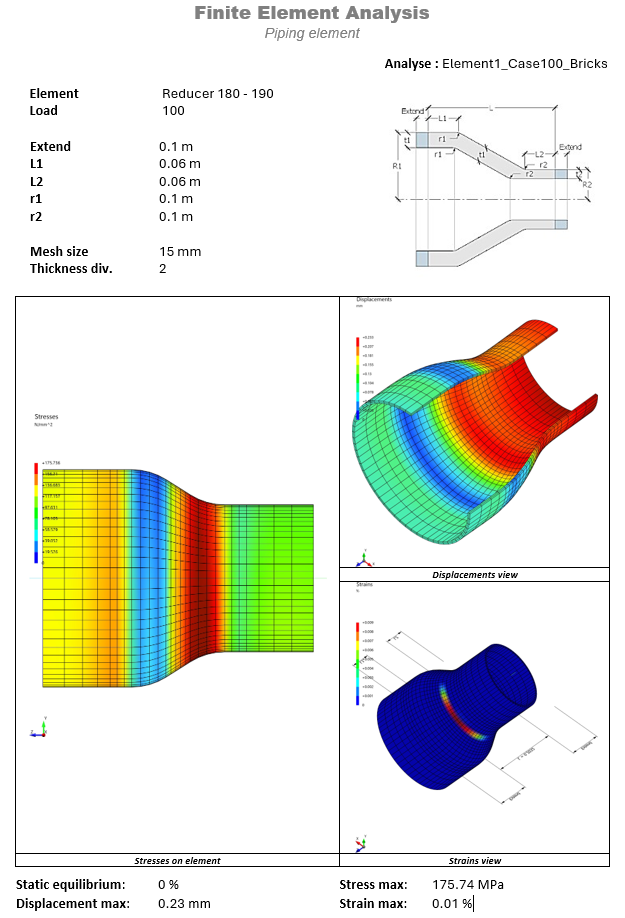
Example of document :
6. Conclusion
The analysis is terminated.
You can keep this analysis on disk by closing the window and answer Yes to the question :
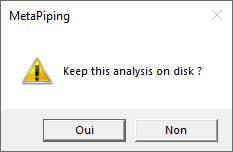
This analysis will be proposed on the window of §1 for the same element, load and template.