Bend analysis
MetaPiping proposes a detailed analysis of bend.
After piping analysis, the bends can be examined.
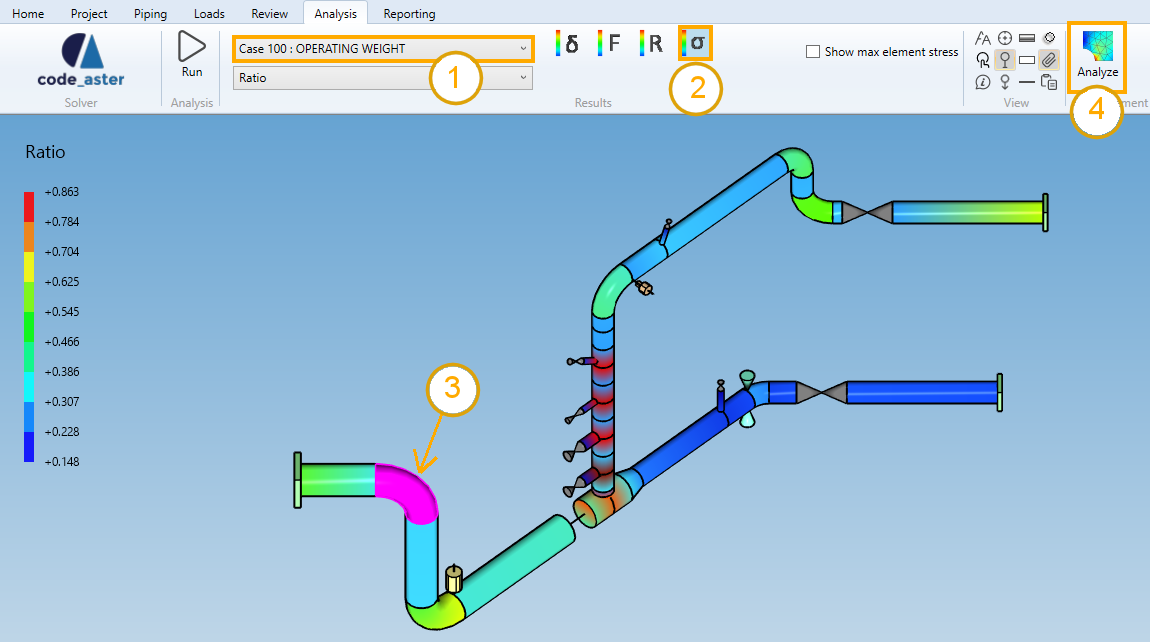
- Select a load case or mode (1).
- Select the stress button (2).
- Select either a bend in the 3D space or in the results table (3).
- Click on the Analysis button (4).
The selection mode is automatically set to Element when clicking on stress button.
1. Template
You can then choose a template of Finite element :
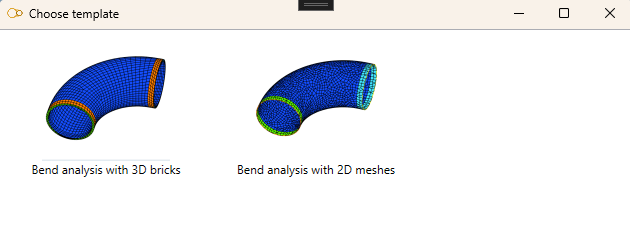
- 3D bricks : second order 20-node hexahedrons for curved volumetric element
- 2D meshes : second order 8-node quadrangles for curved surface element
If other analysis exists for the same Element, the same Load and the same Template, a window will appear.
Example for a pipe analysis (same window for bends) :
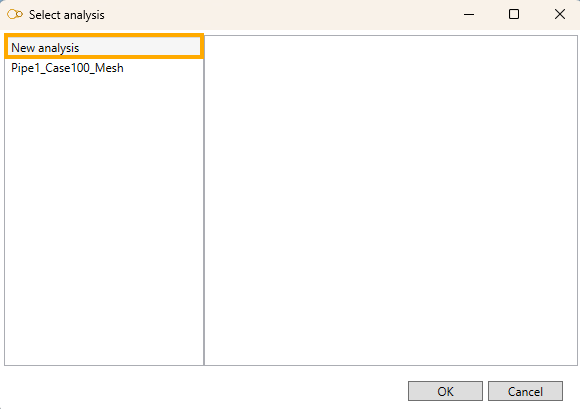
- Select New analysis to start a new analysis from scratch.
- Or select an existing analysis to reopen it :
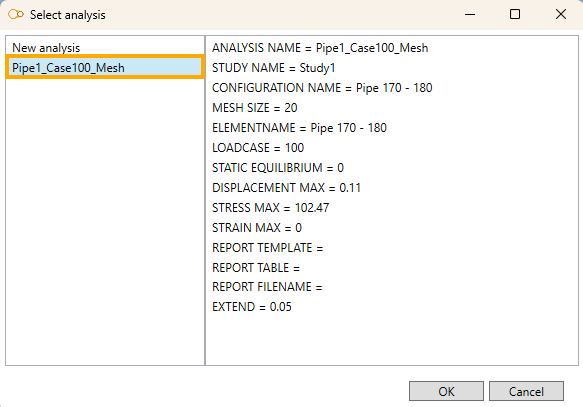
Some properties and results are shown.
Click OK.
2. New analysis
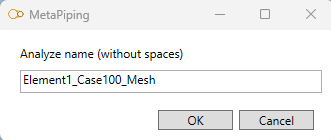
If you choose to create a New analysis, you have to define a name to the analysis (that doesn’t already exist) :
The Finite Element Analysis Window appears (2D mesh template).
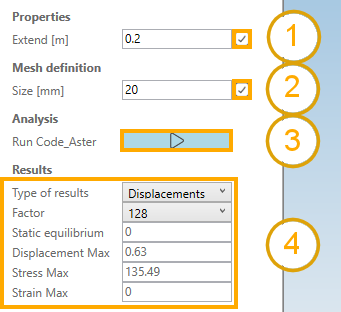
- Set Extend = 0.2 m and click on (1)
- Set Size = 20 mm and click on (2)
- Click on Run Code_Aster (3) to launch the analysis
Results :
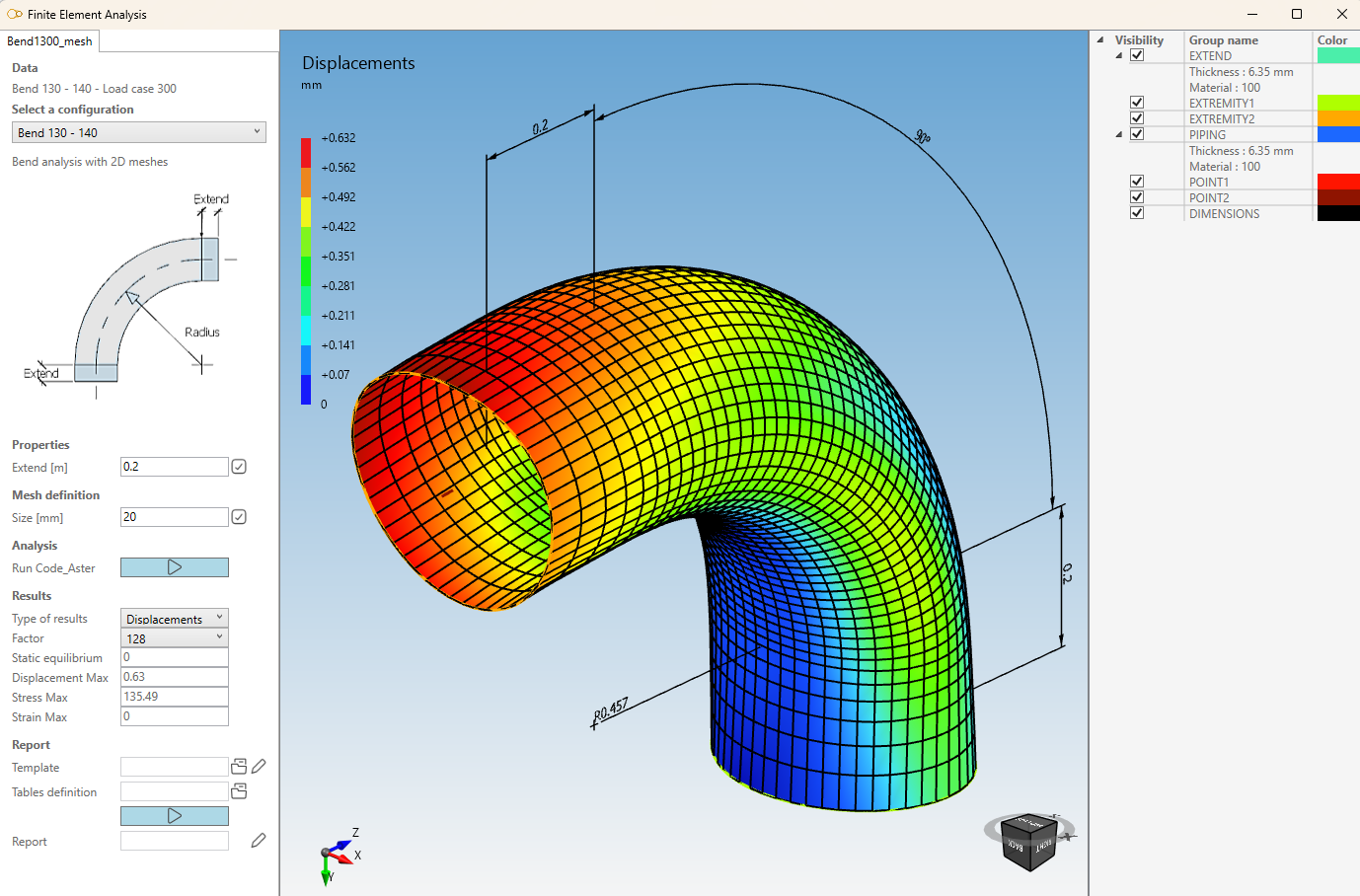
Click here to have more information about this window.
A result panel appears where the type of results can be choose and some informations are shown (4).

Type of results :
| Property | Unit Metric | Unit USA | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|
| Groups | - | - | |
| Displacements | mm | in | Use Factor to amplify the deformation |
| Stresses | N/mm² | ksi | |
| Strains | % | % | |
| Iso-displacements | mm | in | Use Factor to amplify the deformation |
| Iso-stresses | N/mm² | ksi | |
| Iso-Strains | % | % |
The Static equilibrium is also evaluated (value near 0 reaches the perfect equilibrium).
Static Equilibrium refers to the physical state in which a system is at rest and the net force acting
on it is null. It is a state in which all the forces acting on an object are balanced out and the
object is not found to be in motion to the relative plane.
3. Report
Click here to have more information about the report mechanism.
4. Brick template
If you select the Brick template, some features change :
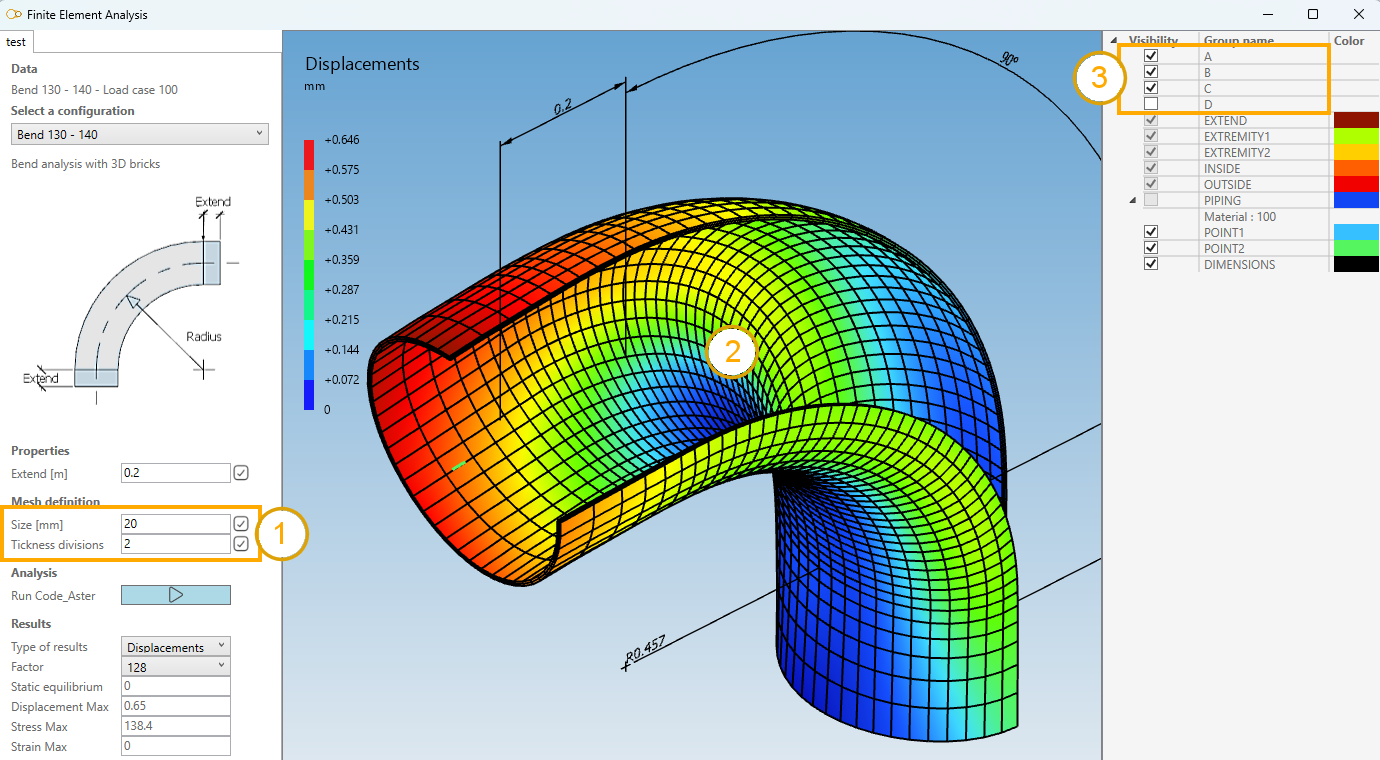
The mesh definition contains also the thickness division (= number of element in the thickness) and 4 groups that enable to hide part of the assembly (A, B, C and D).
In this example, you can see (2) a thickness division = 2 (1) and group D hidden to see the interior of the element.
5. Conclusion
The analysis is terminated.
You can keep this analysis on disk by closing the window and answer Yes to the question :
This analysis will be proposed on the window of §1 for the same element, load and template.